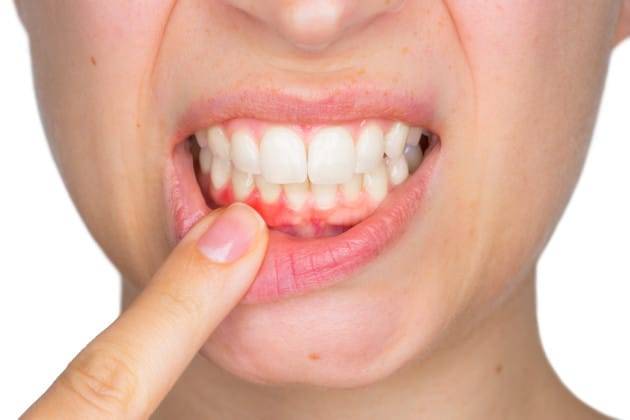
What is gum disease?
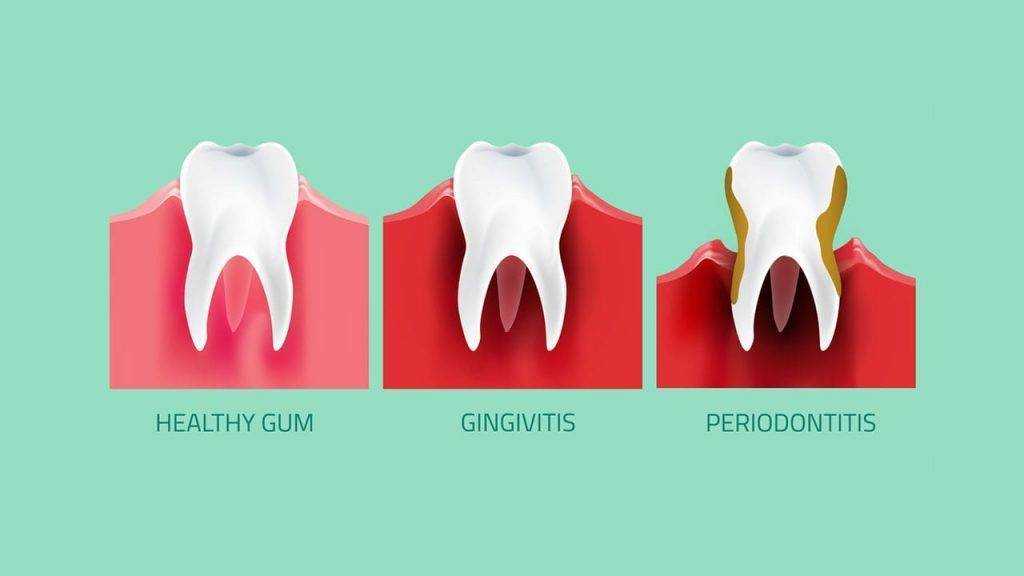
Gum disease means pain and infection of the tissues supporting the teeth. There are mainly two forms of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontal disease.
What is gingivitis?
In Gingivitis inflammation appears in gums. This is when the gums around the teeth turn red and swollen. This swollen gum often bleeds when you are brushing.
Gingivitis is a gum disease where the gums show symptoms like swollen gums and bleeding. The gum diseases like Gingivitis are of different types. Different types of gingivitis are Actinomycotic Gingivitis, Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis, Pregnancy Gingivitis, and Diabetic Gingivitis. All these give the same gum problem symptoms that are problematic for gums.
What is periodontal disease?
When gingivitis stays a long time in the mouth it can turn into periodontal disease. There are various types of periodontal disease that affect the gums and tissues supporting the teeth.
As the disease continues the bone anchoring the teeth in the jaw can be lost. This makes the tooth loosen. If it is left untreated teeth may eventually fall out. In fact, more people lose their teeth through periodontal disease than through tooth decay.
How can I access my risk of Gum disease?
Many people suffer from some form of gum disease, and it is the major cause of tooth loss in adults. However, gum disease spreads slowly, If it is treated in time then your teeth and gums can be saved.
What is the cause of gum disease?
All gum disease is caused by plaque. Plaque is produced by bacteria that forms on the outer layer of the teeth and gums every day. Many of the bacteria in plaque do not harm. But some of that has been found to be the main cause of gum disease. To prevent t gum disease, you need to remove all the plaque every day by brushing and flossing.
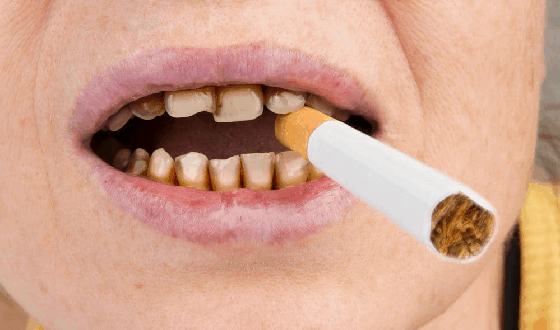
How will smoking affect my gums and teeth?
Smoking can worsen gum disease. People who smoke are more likely to produce more bacterial plaque. The gums will be affected because smoking causes a lack of oxygen in the bloodstream.
So the infected gums are unable to heal. Smoking allows to form more dental plaque and for gum disease to progress more fastly than in non-smokers. However, it still remains the most common reason for tooth loss in adults.
What happens if gum disease is not treated?
Unfortunately, gum disease develops without showing a sign of pain so that you do not notice the damage. However, bacteria are sometimes more active and cause soreness.
Further, it can lead to gum abscesses, and pus may ooze from gum tissues and surrounding bones. As the disease continues over the years supporting bone will be damaged and teeth can be lost. If the disease is not treated for a long time, treatment can become more difficult.
How do I know if l have gum disease?
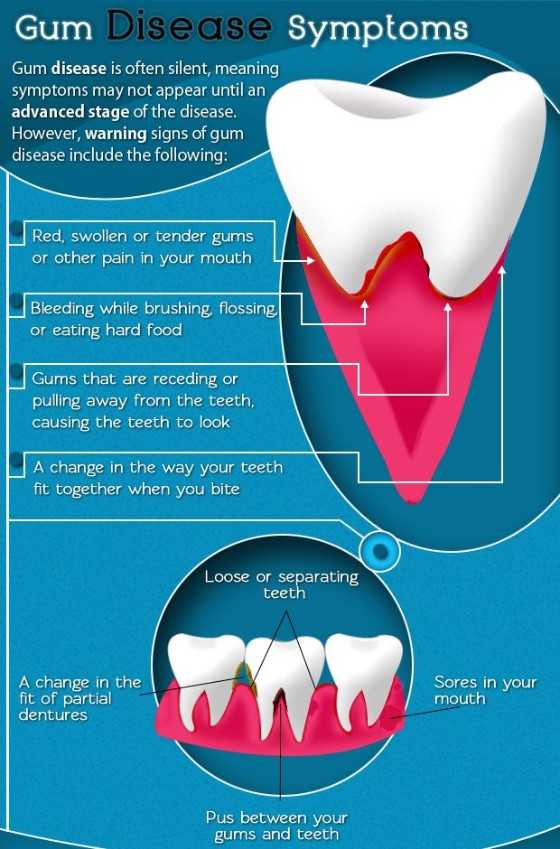
The first sign of gum disease is blood while you are brushing or rinsing. You may find blood also when you are eating, leaving a bad taste in your mouth. You may notice an unpleasant. breath also.
What do I do if think I have gum disease?
The first thing to do is to visit your dentist for a dental check-up. The dentist can measure the ‘cuff ‘ of gum around each tooth and can see if there is any sign that periodontal disease developing. X rays may also be incorporated to see the amount of bone has damaged. This assessment is very important, so the correct treatment can be prescribed then after.
What treatments are needed?
Your dentist will usually clean your teeth. They also remove plaque cleaning all surface of your teeth thoroughly and effectively. This may take a few sessions with your dentist
What else may be needed?
Once your teeth are clean, your dentist may start further cleaning of the roots of the teeth, to ensure that the last pockets of bacteria are removed. This is also known as root planning. You may need the treatment area to be numbed before the procedure. Afterward, you may feel some discomfort for up to 48 hours.
Once I treated periodontal disease, can I get it again?
The periodontal diseases never cured. But as long as you maintain oral care further loss of bone will be very slow and it may stop altogether. However, you must remove plaque every day, and go for regular check up by the dentist and hygienist.
Is Gum Disease Linked to Other Health Problems?
As indicated by the dental specialists, dentists have revealed potential connections between gum infection and different genuine wellbeing conditions. In individuals with solid insusceptible frameworks, the microbes in the mouth that advance into the circulatory system are generally innocuous.
Yet, in specific situations, these microorganisms are related to medical issues, for example, stroke and coronary illness. Diabetes isn’t just a hazard factor for gum infection, however, gum malady may aggravate diabetes.